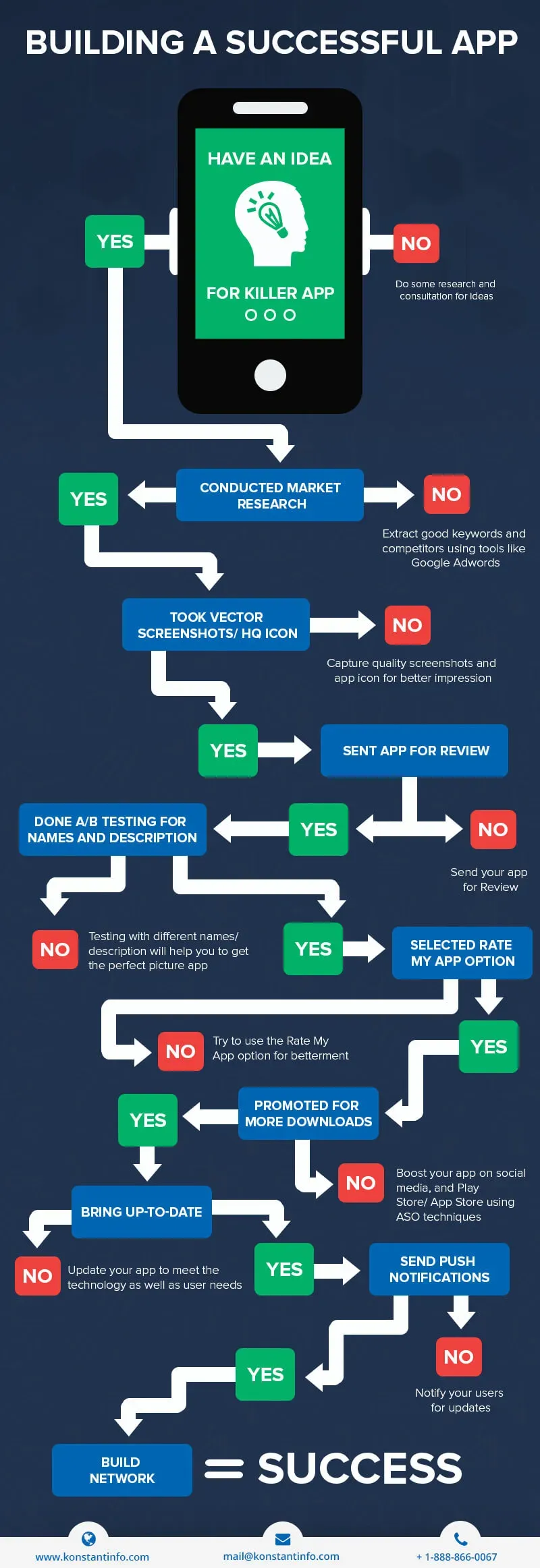
To build a successful app, you start with a clear problem, a defined audience, and a plan that covers the core steps of the app development process. From ideation to delivery, focusing on validating an app idea early helps you test assumptions before heavy investment and shapes your minimum viable product. A practical path combines thoughtful user onboarding for apps with a mobile app launch checklist to ensure you capture early feedback and measure real impact. By prioritizing the MVP, mapping user journeys, and iterating after release, you align product value with performance realities and stay focused on sustainable growth. Ultimately, a disciplined approach rooted in user empathy, continuous validation, and transparent metrics turns ideas into a scalable, user-loved app.
Viewed through the lens of product discovery, turning an idea into a successful software solution involves ideation, rapid prototyping, and early market validation. This approach emphasizes testing hypotheses with lightweight prototypes, refining the value proposition, and aligning teams around a lean MVP. A robust launch strategy depends on a clear go-to-market plan, intuitive onboarding, and strong analytics to gauge adoption and retention. By framing development as an iterative cycle from concept to scalable mobile application, you keep momentum while learning from real users. In essence, sustainable product success comes from continuous discovery, validated learning, and disciplined execution across the app lifecycle.
Validating an App Idea and Defining the Problem for a Strong App Development Process
A successful app starts with clarity: a well-defined problem and a precise audience. By articulating the issue in a customer-centric way, you create guardrails for feature selection, UI design, and success metrics. This foundational step anchors every decision in the app development process, ensuring that every subsequent choice serves the people you’re trying to help and that the product remains focused rather than feature-creep prone.
With a clear problem statement and audience in mind, you can approach validation more efficiently. Validating an app idea becomes a structured activity: lightweight market research, quick competitor analyses, and candid conversations with potential users. By testing a concise set of assumptions with a small, representative group, you gain confidence to proceed and set up a realistic plan. This disciplined approach to validation helps you avoid building something nobody wants and strengthens your readiness to move toward a minimum viable product.
Ultimately, this phase primes you for a focused MVP that demonstrates value to early adopters. Framing the problem well also guides decisions about scope, critical features, and the core user flow, laying the groundwork for the MVP to be both testable in the wild and expandable as you learn from real usage. In short, a well-validated problem and audience are the bedrock of a durable app development trajectory.
Build a Successful App: From Minimum Viable Product to a Mobile App Launch Checklist
Transforming insight into a tangible product begins with designing a minimum viable product that delivers core value quickly. The MVP should address the riskiest assumptions with a lean feature set, a clear value proposition, and a testable user flow. This stage is not about perfection; it’s about learning fast from real usage so you can iterate efficiently and steer the product toward real market fit within the broader app development process.
With the MVP in hand, the focus shifts to planning for a successful launch. A comprehensive mobile app launch checklist covers QA rigor, performance monitoring, metadata optimization, and localization as needed for different regions. Equally important is ensuring user onboarding for apps is smooth and informative—teaching value early and reducing friction to activation. By syncing the MVP’s learnings with a structured launch plan, you set the stage for early feedback, improved retention, and a scalable growth trajectory.
After launch, continuous improvement becomes the ongoing rhythm. Track activation, retention, and engagement metrics, and use qualitative feedback from onboarding experiences and in-app analytics to refine features and flows. This iterative discipline completes the lifecycle from MVP to a robust product, reinforcing the importance of the app development process and a deliberate, data-informed approach to growing a successful app.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I build a successful app by following the app development process and validating an app idea early?
To build a successful app, start with a clear problem and audience. The app development process emphasizes validating the idea with real users—conduct lightweight interviews, share a simple prototype, and measure willingness to adopt. Develop a minimum viable product (MVP) that delivers core value and lets you learn from real usage. Include user onboarding considerations so early users quickly experience value. With these steps, you minimize risk, learn fast, and set the stage for iterative improvements and long-term success.
What role does a mobile app launch checklist play in building a successful app, and how does it connect with validating an app idea and an MVP?
A mobile app launch checklist ensures readiness for release, covering QA, performance monitoring, store assets, metadata, localization, and rollout strategy. This practical checklist helps validate an app idea in the market by aligning launch readiness with measurable goals and user feedback. Pair the checklist with a minimum viable product to launch quickly, gather usage data, and iterate. Post-launch analytics on activation, retention, and onboarding guide ongoing improvements, keeping your work aligned with the broader app development process and growth objectives.
| Stage | Focus | Key Activities | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Introduction | Idea to market: spark to real users | Understand the problem, validate the idea with potential users, and define a focused minimum viable product (MVP) to test in the wild | Foundation for decision-making and user-centric product development |
| 1) Start with a clear problem and audience | Problem clarity and audience definition | Articulate a customer-centric problem, define the audience/personas, and set guardrails for features, UI, and metrics | Guides decisions and simplifies validation |
| 2) Validate the idea before heavy investment | Structured validation | Lightweight market research, competitor analysis, and real conversations with potential users; interviews, prototypes, and measuring reactions | Increases confidence to proceed and avoids building unwanted products |
| 3) Define your minimum viable product (MVP) | MVP design and prioritization | Identify the smallest set of capabilities that delivers value; prioritize must-haves using impact vs. effort; define core user flow and analytics; plan iteration | First concrete test of the app concept and a pace for future improvements |
| 4) Plan the user experience and architecture | UX and technical foundation | Map user journeys, create wireframes, design onboarding; decide native, cross-platform, or PWA; outline scalable backend and APIs; secure data practices | Balanced product/tech plan that supports growth |
| 5) Build with an iterative mindset | Iterative delivery and learning | Work in sprints; release the MVP and iterate from feedback; use feature toggles, A/B testing, and CI/CD | Sustainable velocity and continuous improvement |
| 6) Quality assurance and testing as a first-class activity | Quality and reliability | Unit, integration, and end-to-end tests; real-world device/conditions; beta testers; clear acceptance criteria; automation where practical | Robust QA with positive impact on retention and ratings |
| 7) Launch planning: a mobile app launch checklist | Launch readiness | Final QA sign-off, monitoring plans, and a plan for communication; prepare store assets, metadata, and localization; choose phased rollout vs. full launch; set analytics for acquisition, activation, retention, revenue | Increases visibility, rankings, and accelerates feedback-driven iteration |
| 8) Marketing, monetization, and growth levers | Growth and monetization strategy | Content marketing, social proof, partnerships, ads; define a monetization model; plan retention via onboarding, updates, and in-app messaging | Aligned growth efforts with user value and revenue potential |
| 9) Post-launch iteration and continuous improvement | Ongoing optimization | Track metrics (activation, DAU, session length, churn, LTV); gather qualitative feedback; prioritize next features | Sustained growth through adaptation to user needs and market shifts |
| 10) Common pitfalls to avoid and best practices | Risk awareness and guardrails | Avoid scope creep, MVP over-engineering, onboarding gaps, and weak data-driven iteration; maintain guardrails, ship small updates regularly | Increases odds of turning an idea into a beloved, successful app |
Summary
Conclusion: From idea to launch, building a successful app requires a blend of user empathy, validated learning, disciplined MVP design, and deliberate execution. By following a structured process, prioritizing onboarding and user experience, and embracing iterative improvements, you create a product that not only launches smoothly but continues to grow and adapt to user needs. The journey is ongoing: the most valuable learnings come after the initial release, when real users engage with your app every day.