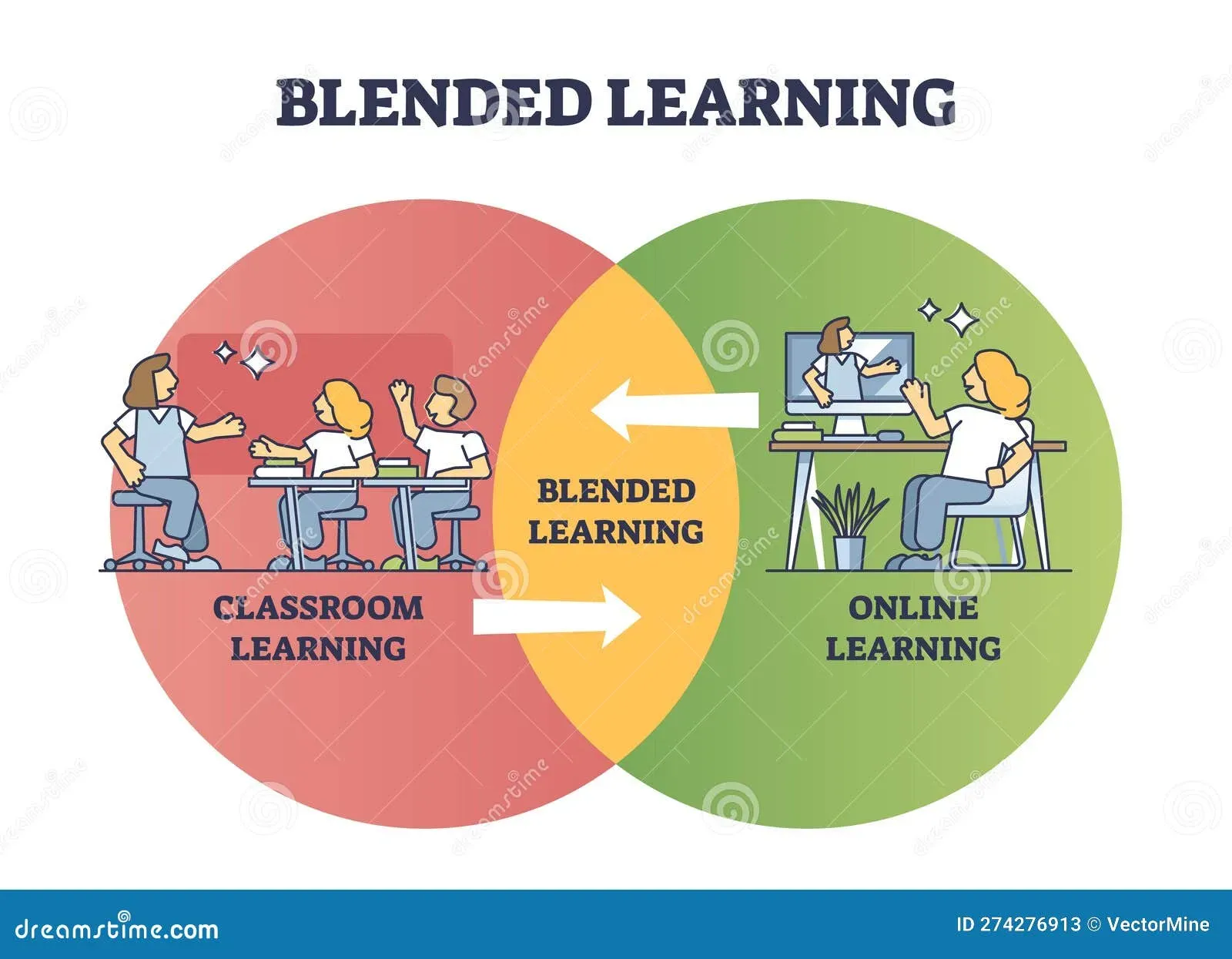
Blended Learning is transforming how students acquire knowledge by weaving together online learning with in-person instruction to create a more flexible, student-centered experience that supports cloud-based resources, diverse assessment methods, rapid feedback loops, and reinforces teachers’ planning, cross-curricular integration, and flexible pacing across different cohorts, campuses, and learning environments, ultimately strengthening instructional consistency while allowing local adaptation to student needs. This approach unlocks many blended learning benefits, such as personalized pacing, increased access to resources, and the ability to tailor instruction while preserving collaboration across teams, clubs, and subject-area cohorts. Educators can experiment with hybrid learning strategies that blend digital modules with hands-on practice, making classroom technology a powerful catalyst for active exploration, real-time feedback, mastery-based progression, and inclusive participation. In this model, students navigate online learning tasks at a pace that suits them and then apply concepts through guided discussion and project work, boosting student engagement in blended learning as they connect ideas, solve problems, and communicate insights. When thoughtfully designed, Blended Learning expands access, improves outcomes, and equips teachers to monitor progress and adapt support across disciplines, ensuring that digital components enhance rather than replace meaningful human interaction, and this equity-centered approach helps ensure every learner can progress, regardless of background.
Seen through an alternative lens, this approach is about integrating digital content with in-person collaboration to form a cohesive learning ecosystem. In practice, terms such as hybrid education, multi-format delivery, or digitally enabled classrooms describe the same core idea: online modules paired with face-to-face activities to support ongoing assessment and skill development. This perspective emphasizes adaptive pathways, learner autonomy, and the role of teachers as facilitators who orchestrate resources across modalities. By focusing on how different formats complement each other, schools can design experiences that meet diverse needs while preserving clear learning goals and standards alignment.
Blended Learning Benefits: Integrating Online Learning with Classroom Experiences
Blended Learning benefits come from thoughtfully combining online learning opportunities with in-person instruction to create a richer, more flexible learning experience. By blending asynchronous and synchronous activities, students can access tutorials, simulations, and practice problems online, then apply what they’ve learned in the classroom with guidance from teachers. This approach can improve accessibility, personalization, and overall outcomes by leveraging the strengths of both modalities.
The blended approach supports personalization at scale, allowing learners to advance at their own pace while teachers provide targeted supports. With data-informed instruction, educators can monitor progress and tailor interventions, making classroom time more efficient and focused on higher-order thinking. Importantly, blended learning benefits extend to equity and engagement, as online learning components can be accessed anytime, anywhere, supported by classroom technology that enhances collaboration and feedback, which in turn boosts student engagement in blended learning.
Hybrid Learning Benefits: Enhancing Engagement through Classroom Technology and Online Learning
Hybrid learning strategies merge online learning with face-to-face instruction to optimize both independent study and collaborative problem-solving. In practice, students might complete online modules or micro-lessons before class and then participate in guided practice, discussions, and projects during in-person sessions. This deliberate balance helps teachers maximize classroom time for application, feedback, and social learning while maintaining the flexibility of online resources.
By leveraging classroom technology and carefully designed online content, hybrid learning strategies can foster deeper understanding and sustained engagement. Teachers use analytics from online activities to inform pacing, identify misconceptions, and provide timely interventions, ensuring that all students stay on track. The result is a scalable, adaptable approach that supports online learning, strengthens classroom collaboration, and sustains student engagement in blended learning across diverse subjects.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Blended Learning, and what are the blended learning benefits for student engagement and learning outcomes?
Blended Learning combines online learning with in-person instruction to leverage the strengths of both modalities. Its blended learning benefits include personalized pacing, higher student engagement in blended learning, flexible access to resources, and data-informed instruction. By applying hybrid learning strategies and using classroom technology, teachers tailor activities, monitor progress, and provide targeted support to diverse learners.
How can schools implement Blended Learning effectively with online learning and classroom technology while ensuring equity and measuring impact?
Start with clear learning goals and a small Blended Learning pilot. Use online learning resources and classroom technology to balance asynchronous and synchronous activities, applying hybrid learning strategies that fit your context. Ensure equity by providing devices and offline options, align online tasks with standards, and use data dashboards to monitor engagement in blended learning and student progress. Invest in ongoing teacher professional development to refine design and support scalability.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| What is Blended Learning |
|
| Benefits |
|
| Challenges and Considerations |
|
| Strategies for Effective Blended Learning |
|
| Tools, Technologies, and the Role of Classroom Technology |
|
| Case Examples and Practical Implementation |
|
| Implementation Steps for Schools and Districts |
|
| Measuring Success |
|
| The Future of Blended Learning in Education |
|
| Conclusion |
|
Summary
Blended Learning has emerged as a practical, evidence-based approach to education that blends online learning with in-person instruction to create more flexible and engaging learning experiences. By thoughtfully combining digital resources with face-to-face interaction, Blended Learning supports diverse learner needs, improves accessibility, and enables targeted feedback. This approach offers a spectrum of strategies—from flipped formats to data-informed instruction—that can boost student engagement and achievement while maintaining rigor and equity. As schools scale Blended Learning, ongoing attention to teacher training, infrastructure, and inclusive practices will be essential to sustain impact and ensure all learners benefit from the blended model.