Cost of Software Development is a fundamental concern for startups aiming to turn a great idea into a scalable product, because every decision about funding, staffing, and tooling directly feeds the long-term viability of the project. It represents more than a price tag; it captures the potential value the product can deliver over its lifecycle, including how software development ROI and user adoption interact, how quickly it can scale, and how maintenance burdens grow as the platform matures. Balancing upfront expenditure with the expected return on investment requires thoughtful budgeting, clear feature prioritization, risk awareness, and a realistic view of what it takes to move from concept to market while preserving runway, and governance to keep teams aligned and stakeholders informed. In this guide, we’ll break down budgeting strategies, cost drivers, and ROI considerations to help teams allocate funds where they matter most, align development with business goals, and communicate tradeoffs to investors and stakeholders. Whether you’re shaping a minimum viable product or a full-scale platform, understanding cost structure and ROI is essential for sustainable growth, helping teams deliver value faster, reduce waste, maintain quality as the product evolves.
Beyond the phrase Cost of Software Development, the conversation often centers on the true price of building a software product and the long-term financial impact of decisions made today. This perspective reframes expenses as a development budget that includes engineering effort, tools, cloud infrastructure, and quality assurance, as well as the cost of risk and technical debt. By framing the project in terms of budgeting for software initiatives and the expected ROI over time, teams can better forecast cash needs, set milestones, and communicate tradeoffs with investors. LSI-friendly terms such as cost to build software, platform development expenditure, project cost estimation, and early-stage budgeting for tech products help readers connect related concepts and find guidance across related topics.
Cost of Software Development: Budgeting for Startup ROI, MVP Planning, and Long-Term Value
Cost of Software Development is a fundamental concern for startups aiming to turn a great idea into a scalable product. It’s not simply the price tag; it’s the value the product can deliver over its lifecycle. A thoughtful budgeting approach balances upfront expenditure with potential ROI by clarifying which features to build first, the architectural choices that support growth, and how success will be measured at each milestone.
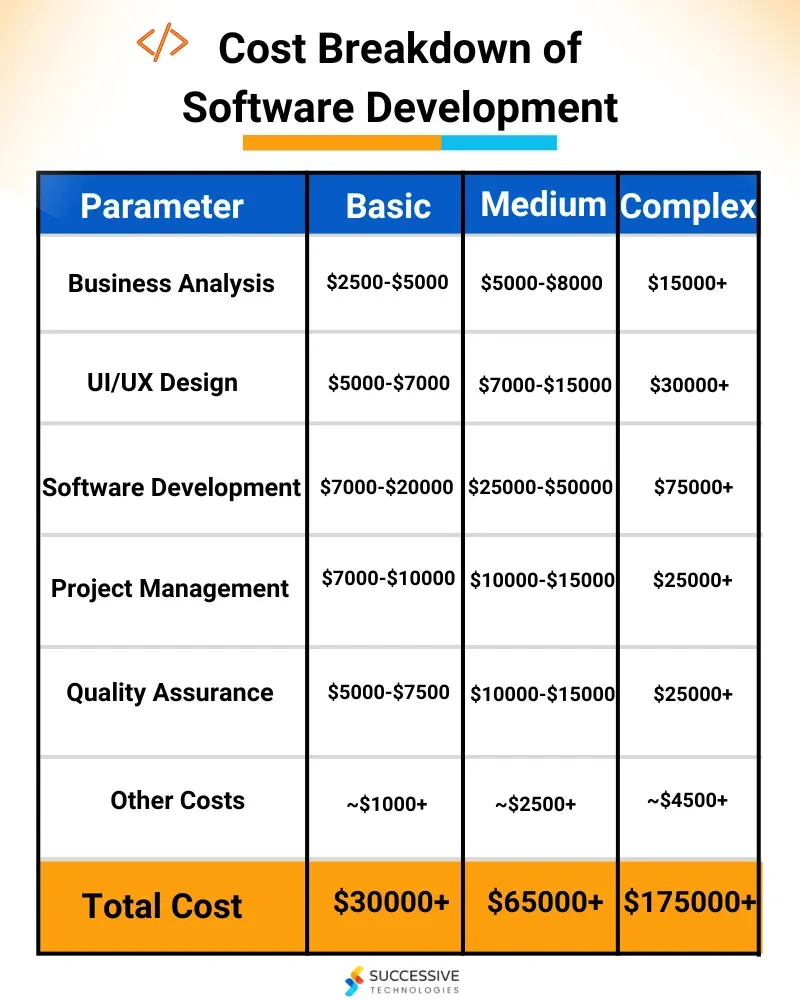
Cost drivers range from personnel and tooling to cloud infrastructure, licensing, security, and ongoing maintenance. A robust budgeting framework maps every cost to milestones, builds in contingencies, and aligns with business goals, enabling smarter decisions about scope, pace, and quality. This is especially important for MVP budgeting and planning, where disciplined prioritization helps maximize software development ROI while preserving runway for future iterations.
Estimation Methods and ROI-Driven Planning for Software Projects: MVP Budgeting and Planning, and Startup Software Budgeting
Estimating costs for software projects is both art and science. For startups, credible estimates blend historical data, expert judgment, and risk buffers. Methods such as top-down budgeting, bottom-up estimation, analog estimation, and three-point estimates help ground budgets in reality and support budgeting for software development and startup software budgeting. Including a contingency helps address uncertainty during MVP budgeting and planning.
ROI remains the north star for startup budgeting decisions. Define keystone metrics, calculate total cost of ownership, and perform break-even analyses to identify features with the strongest ROI signal. A practical budgeting workflow includes defining business goals, drafting MVP scope, selecting engagement models, rolling forecasts, and instituting a metrics-driven review cadence. When cost estimation for software projects is integrated into planning, teams can move faster to value while maintaining quality and strategic alignment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the true Cost of Software Development for a startup, and how does MVP budgeting and planning influence it?
The Cost of Software Development encompasses more than hourly rates. For startups, true cost includes personnel, tooling, cloud infrastructure, licensing, and third‑party services, plus design, QA, security, maintenance, and technical debt. MVP budgeting and planning help control spend by defining the smallest viable scope, prioritizing high‑impact features, and forecasting costs by milestones. A disciplined budgeting approach—covering contingencies, scenario planning, and an appropriate engagement model (time-and-materials, fixed-price, or hybrids)—helps balance upfront investment with potential ROI, preserving runway while delivering a scalable product.
How can startups maximize software development ROI through budgeting for software development and cost estimation for software projects?
Maximizing software development ROI starts with accurate cost estimation for software projects using a mix of top-down budgeting, bottom-up task estimates, analog benchmarks, and three-point estimates to capture uncertainty. Tie spend to ROI by calculating total cost of ownership (TCO) and break-even points, and align features with measurable outcomes. Practical steps include phased delivery, MVP or feature scoping to learn quickly, and rolling forecasts that adjust for risk. Emphasize startup software budgeting practices, automate where possible, and maintain flexibility to reallocate funds based on performance and market signals.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Definition and Purpose |
|
| Cost Components (Direct vs Indirect) |
|
| Budgeting Approach |
|
| Budgeting Strategies for Startups |
|
| Major Cost Drivers |
|
| Estimating Costs |
|
| ROI and Value Realization |
|
| Practical Steps to Optimize ROI |
|
| Budgeting Workflow |
|
| Common Mistakes to Avoid |
|
| Takeaways |
|