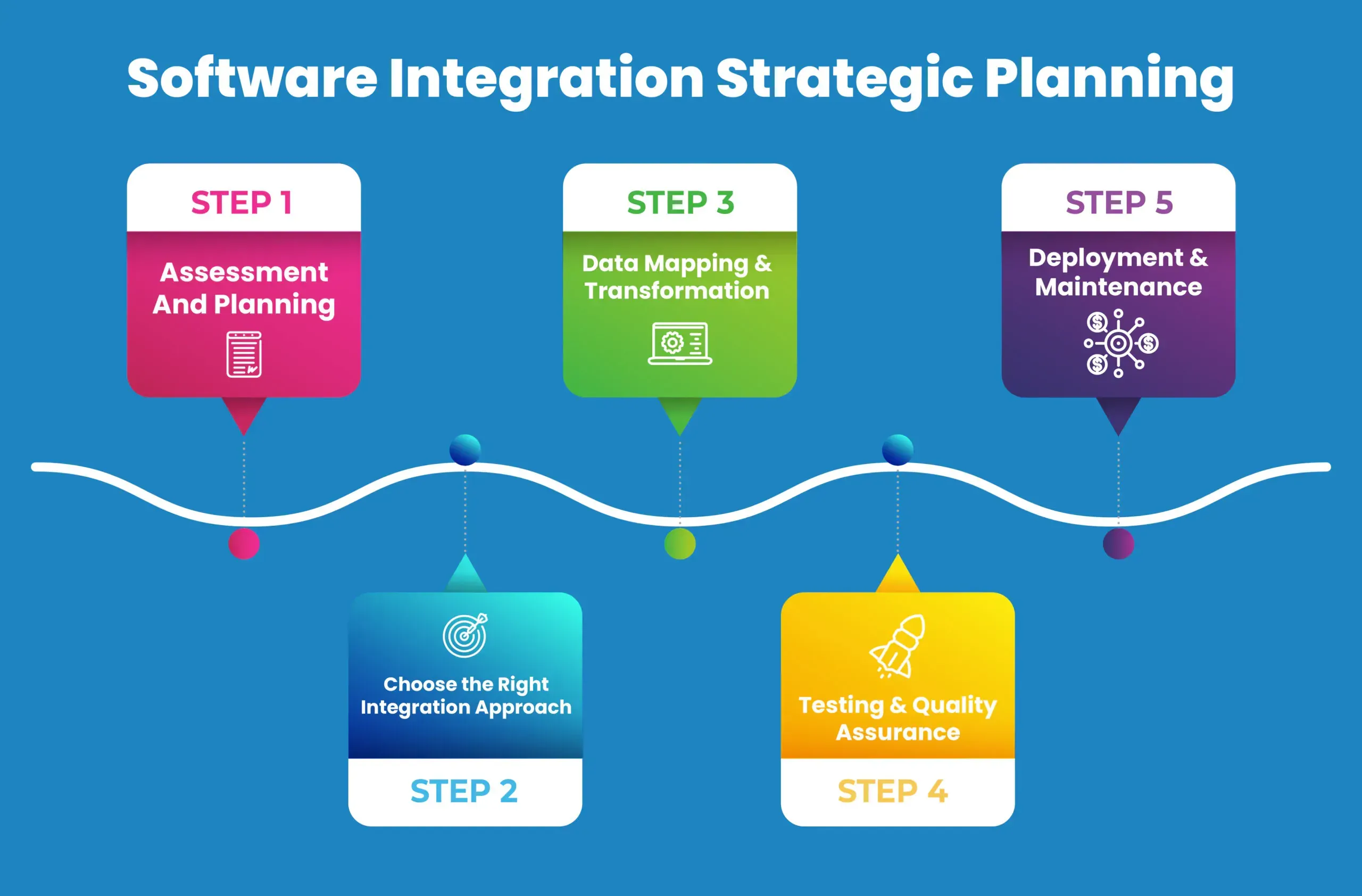
Software integration is shaping how modern teams deliver value by connecting diverse systems, data sources, and services into a cohesive whole, enabling faster decision-making, fewer manual handoffs, and more reliable customer workflows. By embracing a disciplined approach grounded in software integration best practices and a frictionless tech stack, organizations reduce handoff delays, normalize data across domains, and empower developers to focus on new features rather than plumbing. A solid integration strategy enables API integration best practices, scalable data flows, and reliable system collaboration that accelerates time-to-value while supporting governance, security, and composable services. When done right, it unlocks enterprise software integration benefits—clear governance, faster onboarding of tools, and better customer experiences—creating a resilient platform where vendors, partners, and internal teams can operate with shared context. The result is a comprehensive, observable environment where teams ship features with confidence and users enjoy seamless, integrated experiences across applications, networks, and data stores.
In broader terms, this discipline can also be described as system integration and application connectivity, where data moves smoothly between tools without bottlenecks. LSI-friendly phrasing emphasizes the orchestration of disparate platforms, data models, and services into a coherent integration architecture that supports business processes. Organizations often pursue a unified integration landscape that blends middleware, APIs, and event streams to deliver reliable, scalable connectivity across the enterprise. Ultimately, the aim is to harmonize people, processes, and technologies so information moves where it is needed, when it is needed.
Software integration: Creating a frictionless tech stack with API integration best practices
To achieve a frictionless tech stack, organizations must treat software integration as a strategic capability. This means adopting an API-first mindset, standardizing data models, and investing in observability so data can move smoothly between systems—CRM, ERP, marketing automation, and analytics—without brittle handoffs. By following software integration best practices, teams reduce duplication, accelerate onboarding, and increase resilience across the delivery pipeline.
API integration best practices guide the contracts, versioning, and security that keep interfaces stable as the ecosystem evolves. Designing with stable resource names, clear error semantics, and backward-compatible changes enables faster partner onboarding and internal reuse. Coupled with event-driven patterns and a canonical data model, these choices help preserve data quality and enable real-time updates, key ingredients of a frictionless tech stack.
Beyond technology, mapping business goals to an actionable integration strategy ensures you invest in the right connections. Establish governance, ownership, and an inventory of interfaces to prevent drift. When teams share a common view of data, contracts, and outcomes, software integration yields measurable business value rather than endless tinkering.
Enterprise Software Integration: Crafting a scalable integration strategy with governance
When scaling to the enterprise, enterprise software integration requires a deliberate integration strategy that aligns IT capabilities with business outcomes. Start by translating objectives into measurable integration milestones, and set governance for data ownership, schema changes, access control, and regulatory compliance. This strategic approach reduces chaos from point-to-point links and accelerates time-to-value for new initiatives.
Adopt a layered architecture with API gateways, iPaaS, ESB, and lightweight message brokers to unify formats and orchestrate workflows at scale. Use data mapping templates, versioned schemas, and standardized error handling across hundreds of integrations to maintain reliability. This is the essence of enterprise software integration: scalable, auditable connections that support growth without sacrificing governance or security.
Complement technical design with strong security, risk management, and change management practices. Regular security assessments, privacy controls, audit trails, and runbooks for incident response ensure the integration backbone stays resilient as the organization evolves. With robust governance and observability, the integration strategy remains sustainable and capable of supporting future innovations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What constitutes a practical software integration strategy that follows software integration best practices and delivers a frictionless tech stack?
A practical software integration strategy starts with clear goals and a layered architecture that combines API-first design, event-driven data flows, and appropriate middleware. This approach enables a frictionless tech stack by standardizing data models, decoupling services, and ensuring observable, reliable data movement across systems. Governance, data quality checks, and versioned schemas reduce reconciliation effort and speed onboarding of new tools. Prioritize security and robust monitoring from day one to sustain reliability as the ecosystem grows.
What are API integration best practices for enterprise software integration to ensure security, scalability, and maintainability?
Following API integration best practices helps ensure security, scalability, and maintainability in enterprise software integration. Design contracts with stable versioning, consistent resource naming, and clear error handling, and use API gateways to enforce authentication, rate limits, and policy controls. Invest in excellent developer experience with thorough documentation and tooling that simplifies onboarding. Emphasize idempotent operations, reliable delivery, and end-to-end observability to keep integrations resilient at scale.
| Section | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Defines software integration as connecting disparate systems to form a cohesive stack; enables frictionless data flows, automated processes, and reduced manual handoffs; warns against data silos and duplicated effort. |
| Why It Matters | Provides visibility, control, and velocity; reduces manual reconciliation; delivers faster time-to-value, better data quality, improved customer experiences, and stronger governance. |
| Frictionless Tech Stack Concept | Focuses on minimizing friction via standardized data models, documented APIs, robust error handling, and observability to enable easy addition/replacement of services. |
| Build a Cohesive Integration Architecture | Adopt API-first design, event-driven patterns, and middleware (e.g., iPaaS/ESB) to unify data formats and orchestrate workflows. |
| Data Model & Governance | Use a canonical data model; invest in data mapping, normalization, and quality checks; enforce schema versioning, change control, and audit trails. |
| API Design, Management, Security | Contract-driven API design, stable versioning, rate limits, and observable metrics; use gateways for security and policy enforcement; emphasize good documentation. |
| Data Synchronization & Idempotency | Implement idempotent operations, durable messaging, retries with backoff, and appropriate data sync windows; use CDC/event streams for timeliness. |
| Observability, Monitoring, Troubleshooting | Instrument with structured logging, metrics, tracing; centralized dashboards; runbooks and automated remediation where feasible. |
| Security, Compliance, and Risk Management | Embed IAM, encryption, regular security assessments; address data privacy, regulatory obligations, and vendor risk within the strategy. |
| Operational Excellence: Change Management and Collaboration | Foster cross-functional collaboration; align objectives, design, and production stability; maintain a transparent roadmap and continuous improvement culture. |
| Case Studies and Practical Implementations | Example of CRM, marketing automation, and customer service integration using API-first and canonical data model to reduce reconciliation and speed onboarding. |
| Tools, Patterns, and Best Practices | Layered approach with API gateways, orchestration middleware, and event streams; reuse patterns, document decisions, and track ownership. |
| Roadmapping the Integration Journey | Prioritize high-impact, low-risk projects; establish repeatable delivery, with schema registries, interactive API docs, and onboarding automation. |
Summary
Conclusion